
- #XSORT PYTHON HOW TO#
- #XSORT PYTHON SOFTWARE#
- #XSORT PYTHON CODE#
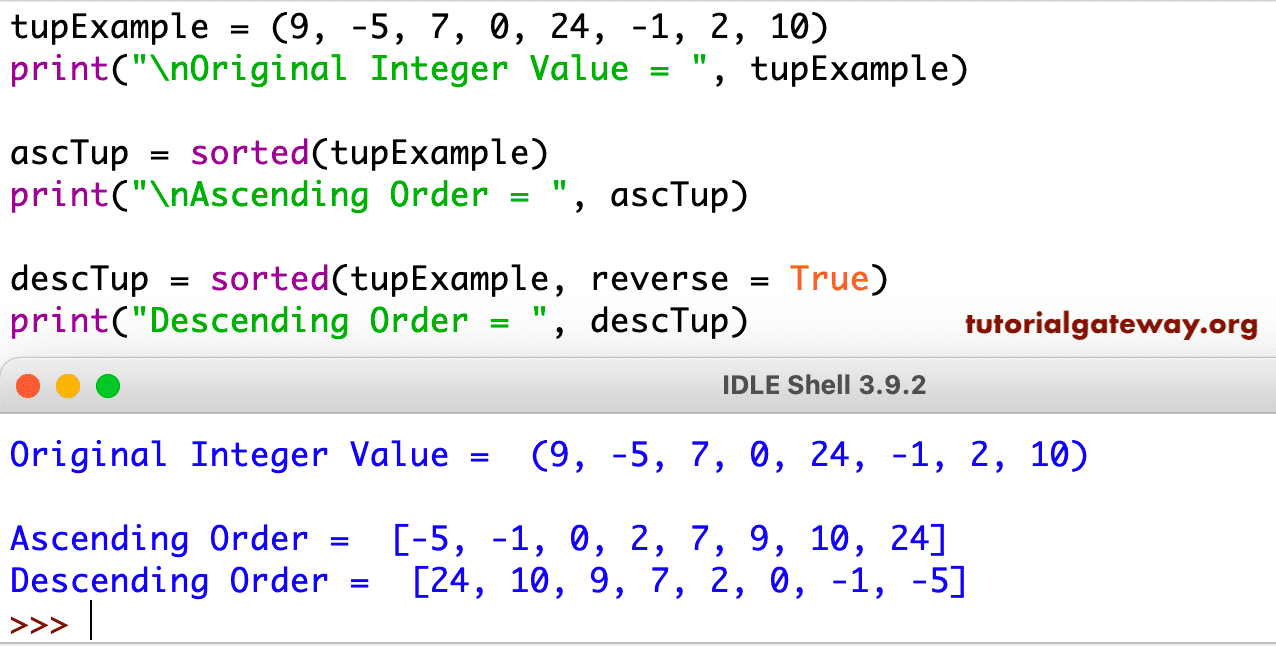
In this example, a list of integers is defined, and then sorted () is called with the numbers variable as the argument: > numbers 6, 9, 3, 1 > sorted(numbers) 1, 3, 6, 9 > numbers 6, 9, 3, 1 The output from this code is a new, sorted list. Now we will try to dry-run this algorithm on an example and see how it affects the sequence. You can use Python to sort a list by using sorted ().
The outer loop will continue to select and place the next smallest items one after the other until the entire list is sorted. After the inner loop, we have found the smallest item from i to n - 1, and it is swapped with the item at i so that it goes to its correct position. Now we compare the item at j to the smallest item we have found yet, and if the item at j is smaller, then it becomes the smallest item we have found yet. There are various types of sorting algorithms in python: Bubble Sort. The comparison operator is used to decide the new order of elements in the respective data structure. Inside, j goes from i + 1 to n - 1, which means that j will point to all the items after i, and it will be responsible to find the smallest item in that range. A Sorting Algorithm is used to rearrange a given array or list of elements by comparing the elements based on some operator. We are considering the item at i to be the smallest one for now, because if we fail to find a smaller element after i, then i holds the correct item. Python’s Built-In Sorting Algorithm The Python language, like many other high-level programming languages, offers the ability to sort data out of the box using sorted (). The role of i is that it will always point to where the next smallest item will go, so we will find the smallest item from i to the end of the list, and it will be placed at i. Now, i goes from 0 to n - 2, which means that i points from the first item to the second-last item. It’s related to several exciting ideas that you’ll see throughout your programming career. 

You may use the following approach in order to sort a list in Python in an ascending order: yourlist.sort () Alternatively, you may use this syntax to sort a list in a descending order: yourlist.sort (reverse True) Next, you’ll see 4 cases of sorting a: List in an ascending order.
#XSORT PYTHON HOW TO#
In this blog, we are going to deal with a quicksort algorithm. How to Sort a List in Python (examples included) July 31, 2021.
#XSORT PYTHON SOFTWARE#
The variable n is the number of items in the list. Sorting is a basic building block that many other algorithms are built upon. From competitive exams to software developer interviews, data structure is an integral part of computer science, the knowledge of basic searching and sorting techniques ( such as bubble sort and merge sort) acts as a building block for data structure and algorithms.This algorithm sorts the list in increasing order, let us see how it works. Explaining the Steps of the Selection Sort Algorithm Notice that the function takes in a list and performs the sorting in-place, it is fairly simple to alter the algorithm to return a sorted list instead.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
